Handel międzyfirmowy
Handel międzyfirmowy to procesy odbywające się pomiędzy firmami w obrębie grupy z tą samą firmą macierzystą. Z perspektywy finansowej zwykle dotyczy to fakturowania, płatności i raportowania.
Dane wyjściowe z procesu handlu międzyfirmowego
Zarejestrowane i uzgodnione faktury międzyfirmowe.
Zarejestrowane i uzgodnione płatności międzyfirmowe.
Łączenie raportów.
Tworzenie faktur wewnętrznych.
Automatyzacja procesów finansowych pomiędzy firmami ulepsza ich przegląd. Księgowania księgi w obrębie grupy są automatycznie rejestrowane z wymiarem handlu wewnętrznego, co umożliwia łączenie i podsumowanie raportów na poziomie grupy.
Zadania, które obejmuje ten proces
Fakturowanie międzyfirmowe – istnieją dwa sposoby fakturowania międzyfirmowego. Faktury sprzedaży wysłane z jednej firmy do innej w obrębie grupy są kopiowane do systemu tej drugiej firmy. W przypadku towarów wysłanych ze wspólnego magazynu wewnętrzne faktury i noty korygujące mogą być tworzone automatycznie. Księgowi w obu firmach muszą następnie ręcznie zarejestrować faktury/noty korygujące we własnym systemie.
Płatności międzyfirmowe – płatności międzyfirmowe dają przegląd przychodzących i wychodzących płatności firmowych, które są połączone z Twoją firmą. Jeśli w systemie firmy brakuje płatności, można je utworzyć w aplikacji płatności międzyfirmowych.
Łączenie raportów – dane finansowe można gromadzić ze wszystkich firm w obrębie grupy. Raporty tworzone w edytorze raportów finansowych mogą być łączone w całej grupie. Struktura konta jednej firmy może zostać zdefiniowana jako wzorzec raportu. Łączenie raportów można również przeprowadzić za pomocą przeznaczonych do tego raportów łączenia. Takie raporty zawierają listę transakcji międzyfirmowych i upraszczają proces tworzenia połączonych kont. W oparciu o początkową konfigurację systemu międzyfirmowego wszystkie transakcje międzyfirmowe będą mogły być automatycznie rejestrowane w Księdze Głównej z dedykowanym wymiarem konta. Umożliwia to raportowanie wszystkich transakcji międzyfirmowych oraz firm powiązanych z każdą z tych transakcji.
Fakturowanie wewnętrzne – fakturowanie wewnętrzne dotyczy fakturowania w obrębie jednej firmy, np. z jednego departamentu do innego departamentu. Sposób przeprowadzania fakturowania wewnętrznego zależy od wymagań firmy dla księgowania kosztów.
[en] Setup for internal invoicing of costs
[en] Enter ICR in the Program field and select the Enter Key to open the ICR menu.
Podpowiedź
[en] If the company using RamBase is part of a corporation, you can set up the other companies in the corporation in the ICR archive. The companies set up in ICR does not have to use RamBase.
[en] The value set up in ICR consists of three letters as an abbreviation for the company and then 2 letters for the country where that internal company is situated. For example XXX-NO for a Norwegian company.
[en] The value set up in ICR is then chosen for the CUS/SUPs (field Intercompany code) that are set up for the internal companies. Documents such as orders/invoices for these internal CUS/SUPs will be marked with the respective Intercompany code.
[en] If relevant GL accounts are set up with Intercompany code = Required/Optional this value will be brought into the General ledger (GL) and the user will be able to pull up reports based on intercompany code. Also, in the Period closure register (PAR), there will be a reconciliation between the internal companies.
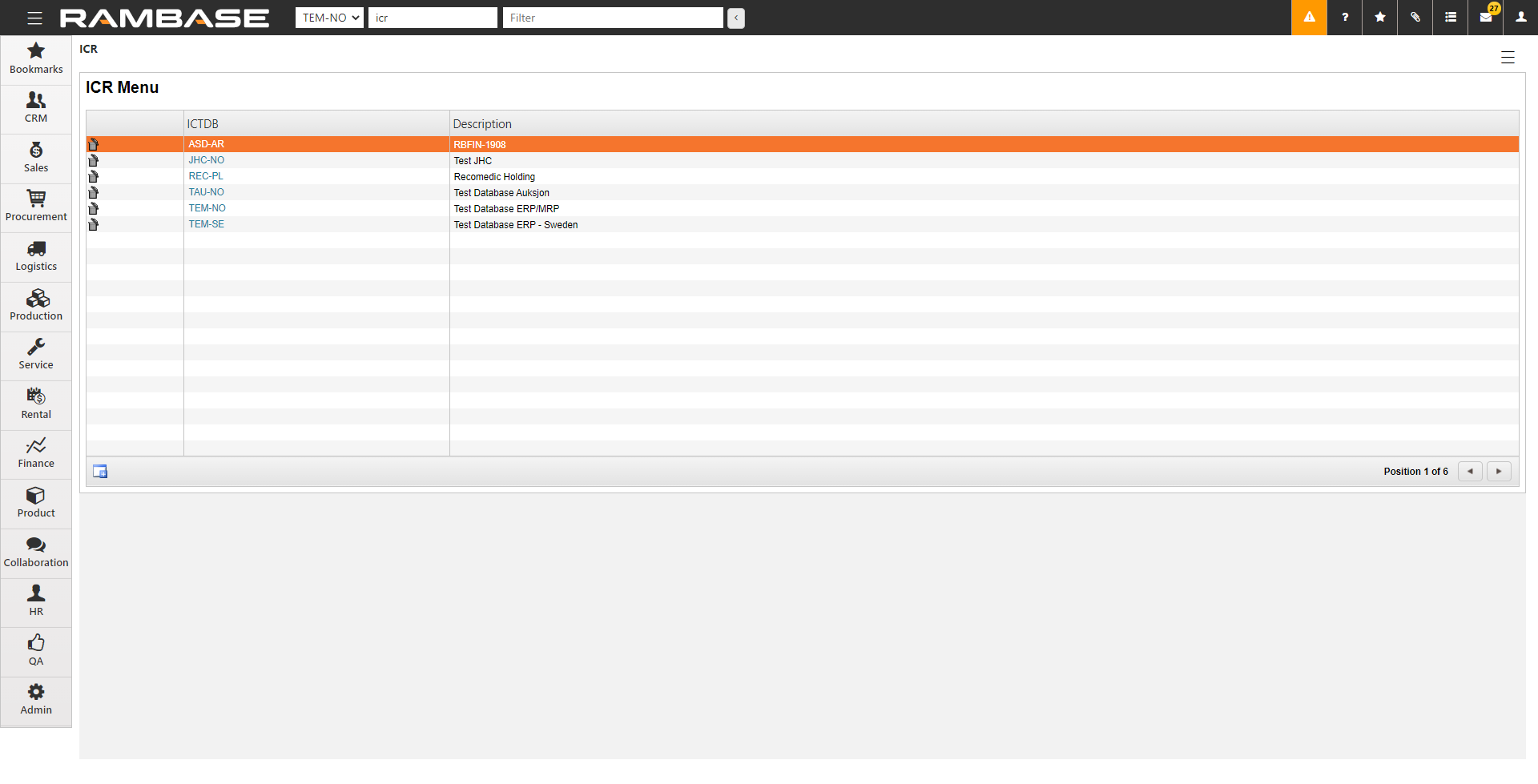
[en] To create a new database, click the Create new button.
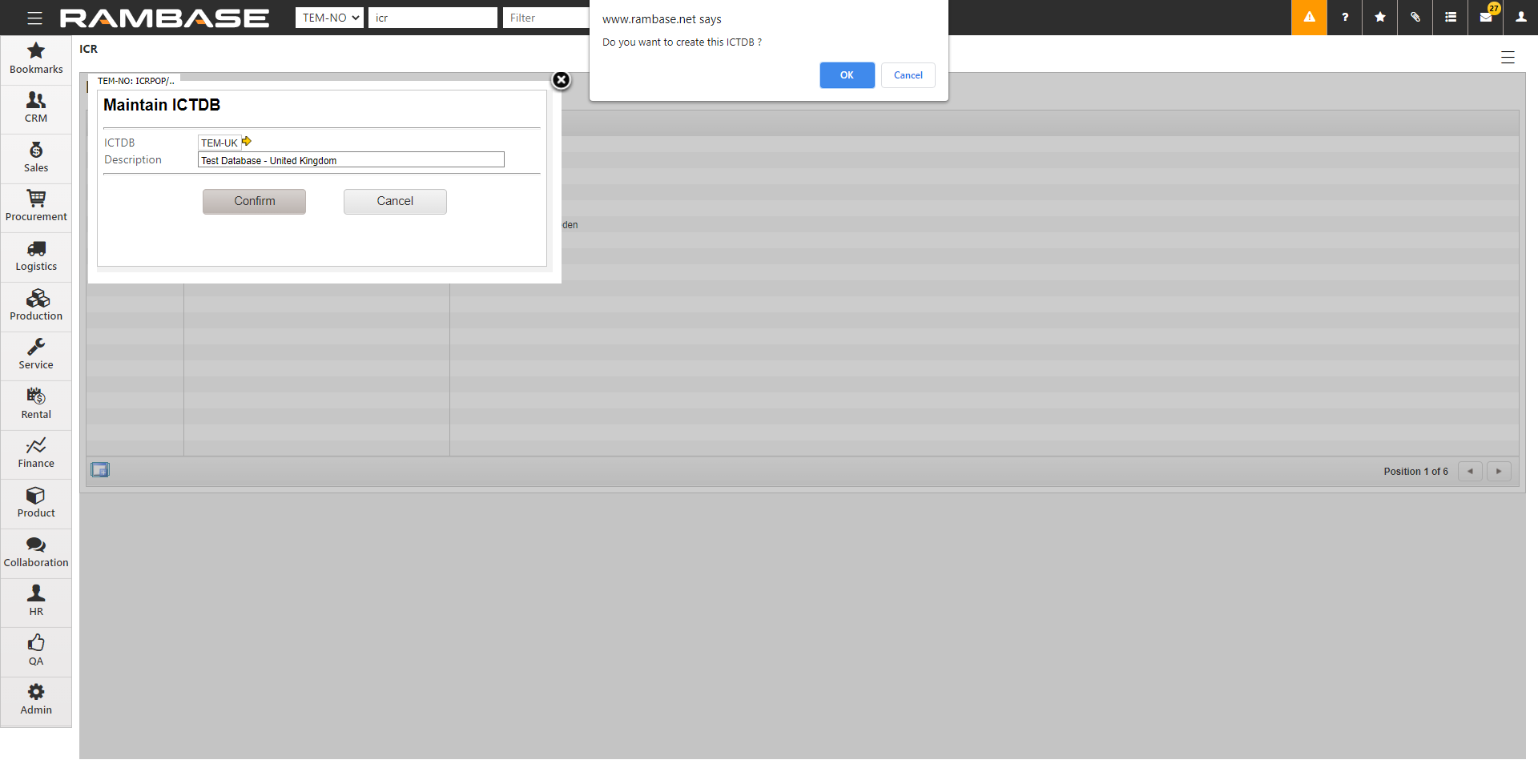
[en] In the ICTDB field, enter the database abbreviation for the other company. This allows you to mark the Customer (CUS) and Supplier (SUP) in the respective database with an inter-company code. You can select the inter-company code in the Customer (CUS) and Supplier (SUP) applications under Settings, then Finance.
[en] Enter ICT in the Program field and select the Enter key to open the Inter Company Trading (ICT) application.
Podpowiedź
[en] If the company using RamBase is part of a corporation, it is possible to set up that outgoing cost invoices, created in one company, should be created as an ingoing invoice in the other company. Companies set up in the ICT archive must use RamBase.
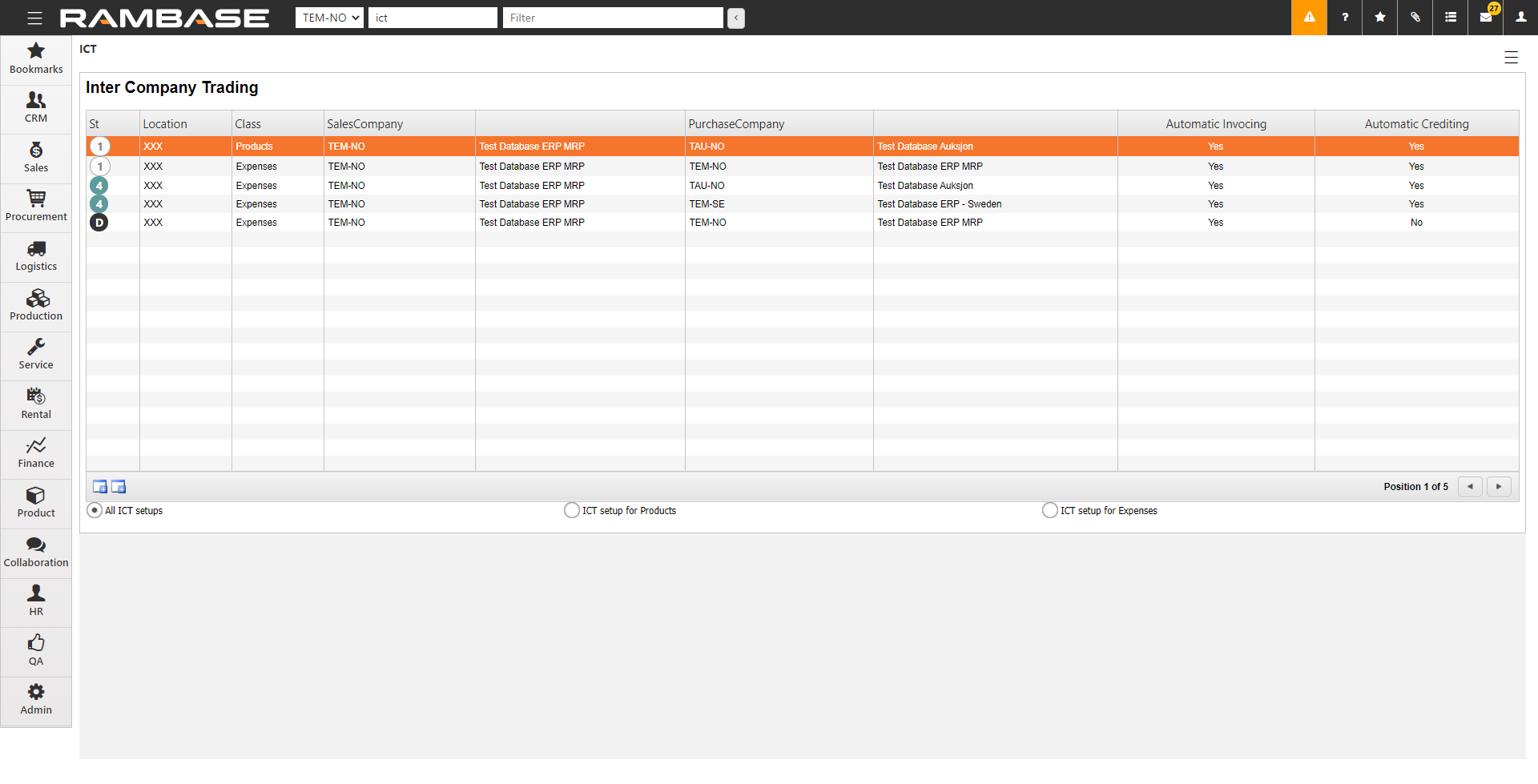
[en] Select the icon on the left, Create ICT setup for Expenses.
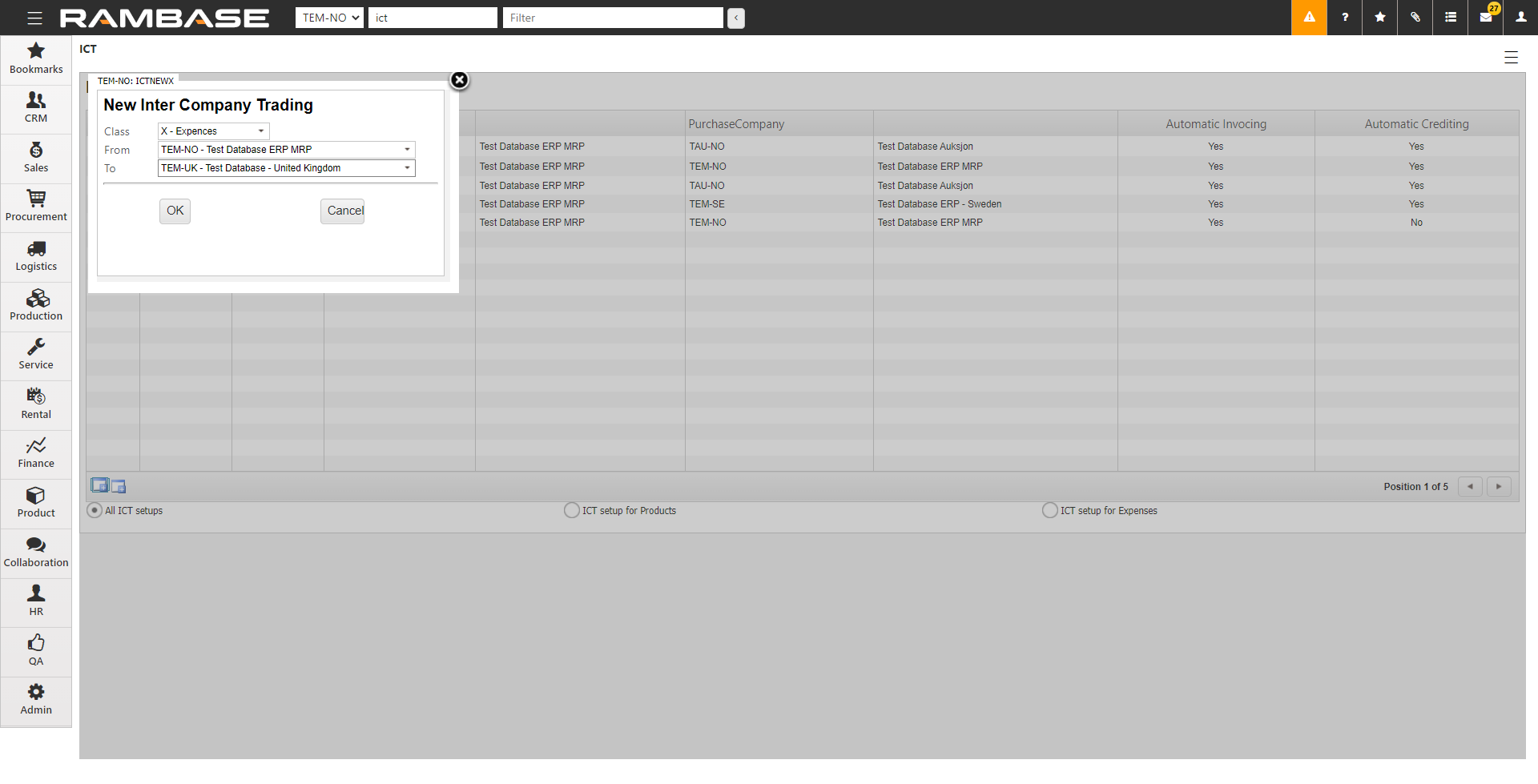
[en] Select the two applicable databases in From and To and select OK
[en] Set Automatic invoicing to Yes.
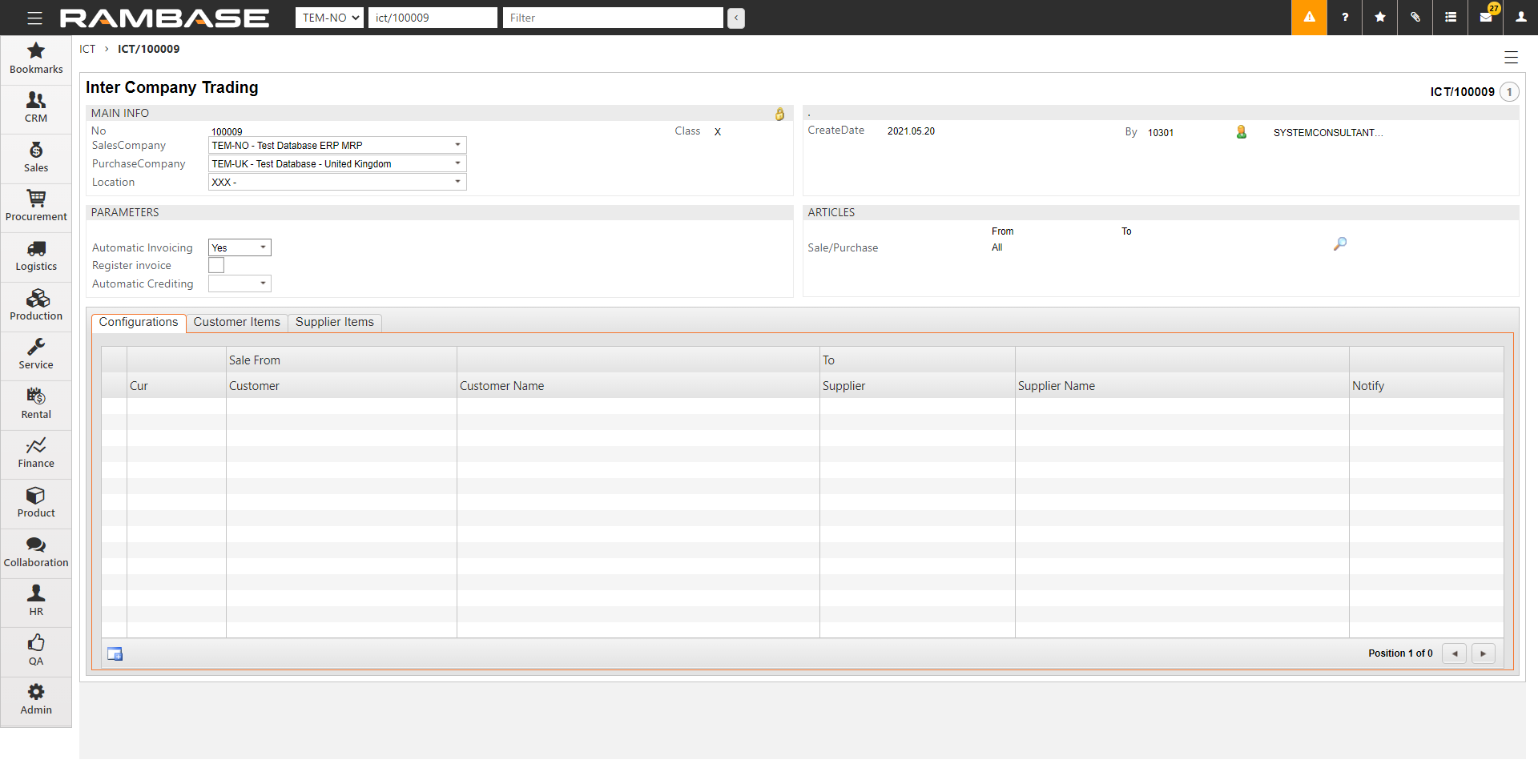
[en] To register the Supplier invoice (SIN) automatically to Status 4 without approval, clear Register invoice. If Register invoice is selected, the Supplier invoice (SIN) remains in Status 1, even if an approval is not required.
[en] Set Automatic Crediting to Yes if inter-company credit should be created automatically.
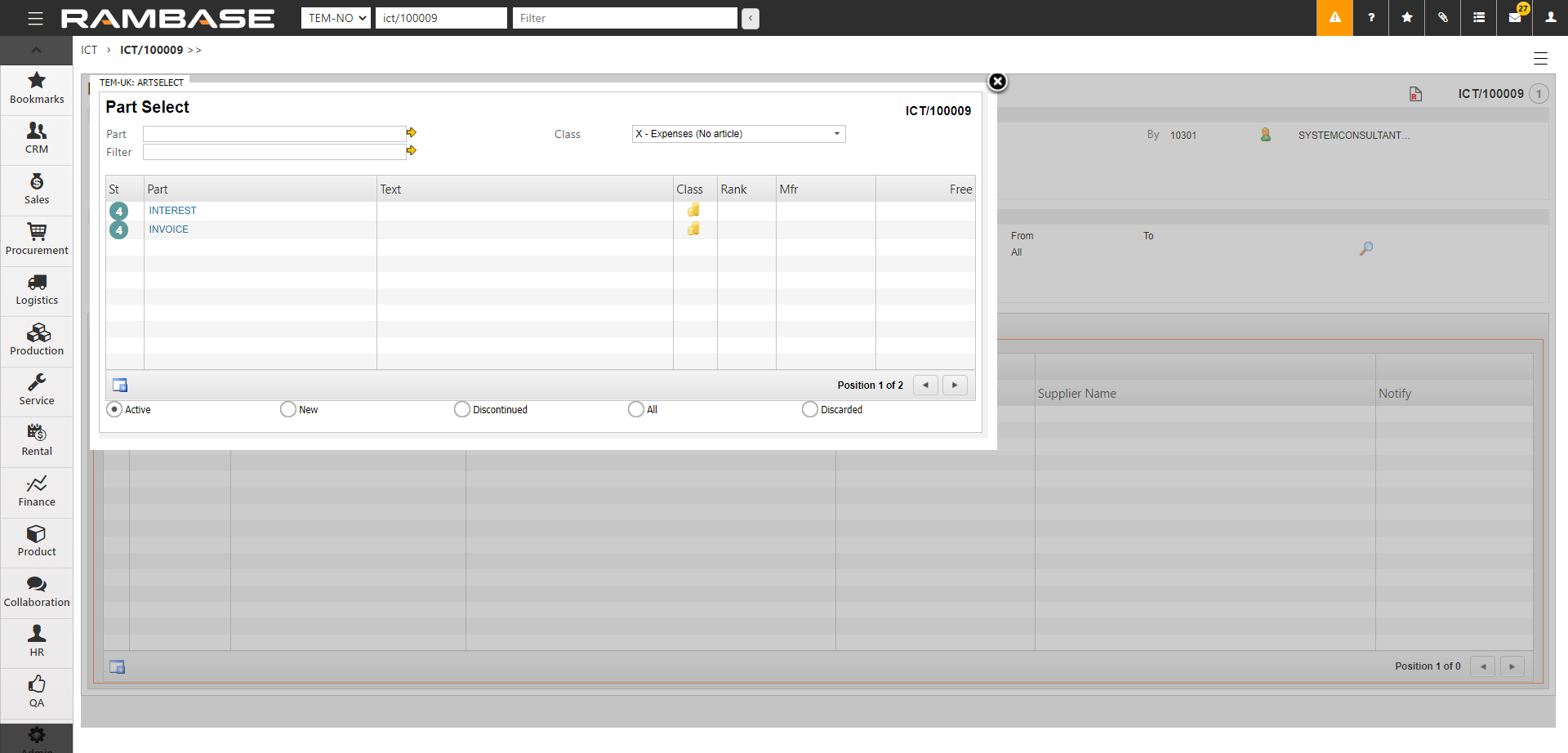
[en] In Articles, select
and specify the article used for nnvoices. This is the article used in the incoming invoices.
[en] In Configurations, select the DEF-line and press the Enter key.
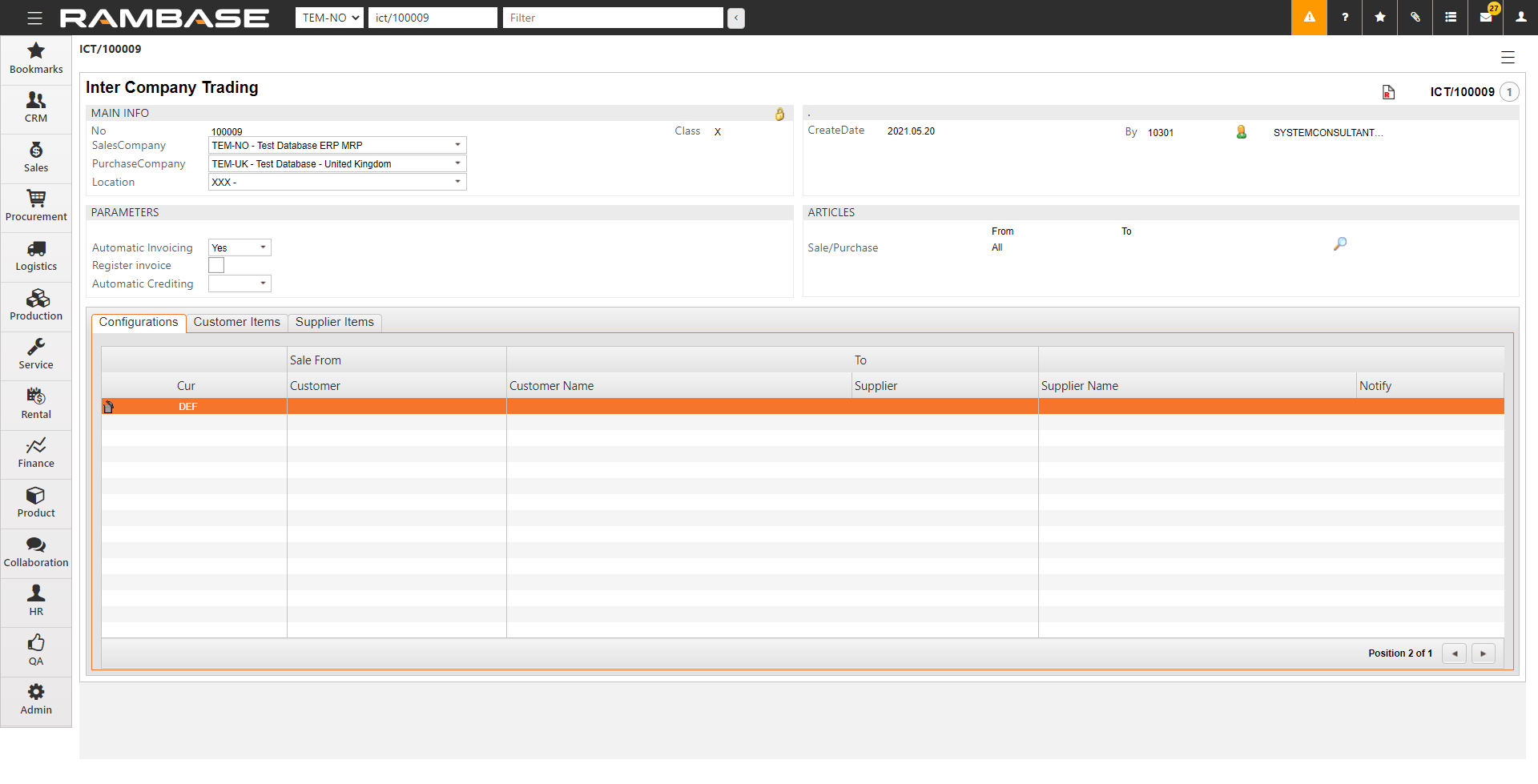
[en] Specify the Customer (CUS) and Supplier (SUP). The correct customer or supplier appears if you have marked them with the inter-company code. If you have not marked the customer and supplier with the inter-company code, do that first.
[en] Set up a Notify PID to specify the user to receive an internal message when a new incoming invoice is created.